New progress has been made in the detection of heavy metal ions
Recently, a research group led by researcher Liu Jinhuai of the Bionic Functional Materials and Sensors Research Center of the Intelligent Machinery Research Institute of the Hefei Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Chinese Academy of Sciences "Introducing Outstanding Overseas Talents" Huang Xingjiu's research group innovatively proposed a new method for detecting heavy metal ions based on molecular gap nanodevice , Realized the specific electrical sensitive response and detection of Hg2 +, and combined with theoretical simulation calculation to clarify its sensitive mechanism. This research result was recently accepted and published by the "Science Report" of "Nature" Publishing Group (Scientific ReportsSci. Rep. 3, 3115; DOI: 10.1038 / srep 03115 (2013)).
Nano-gap devices have become one of the hotspots of current electrical sensor research, and have broad application prospects in achieving highly sensitive detection. In recent years, the research team has been devoted to research in this direction, and has made a series of progress. For example, it summarizes the latest developments and developments in the research direction of nanogap electrodes in sensing and detection (Materials Today, 2010, 13, 28-41); CdSe quantum dots are introduced between nanogap electrodes, with the help of their photosensitivity Characteristics (ultraviolet and visible light), which effectively improves the sensitivity of organic molecule streptavidin detection (Small, 2012, 8, 3274-3281); for the detection of chemically inert PTS, based on the nano-gap electrode, its "inhibition electron" The new principle and method of "transmission" (Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 84, 9818-9824).
On the basis of the above research work, the researchers further introduced the nano-gap device into the detection research of heavy metal ions. By assembling Au nanoparticles filled with glutathione molecular layers between the interdigitated microelectrodes, the construction of molecular gap nanodevices was indirectly achieved. The nanodevice showed a highly sensitive electrical response to Hg2 + and showed a lower detection limit (1 nanometer). However, for other heavy metal ions (such as Zn2 +, Cd2 +, Pb2 +, etc.), the conductance / resistance of the device is not changed. In order to clarify the specific sensitivity mechanism of the nanodevice at the molecular level, the researchers found through theoretical simulation studies: unlike conventional sensor devices, the selectivity of the nanodevice does not depend on the modifier (glutathione molecule) and heavy metals Ion binding capacity. Its sensitive mechanism mainly lies in that after heavy metal ions bridge the glutathione molecules between adjacent Au nanoparticles to form a complex, their frontline orbit distribution and energy are changed, which in turn affects the electronic transport performance of the nanodevice. Undoubtedly, this research work provides new ideas for designing nanodevices with specific and sensitive responses.
The above research work has been supported by the National Major Scientific Research Program, the Chinese Academy of Sciences "Hundred People Program" and Hefei Material Science and Technology Center.
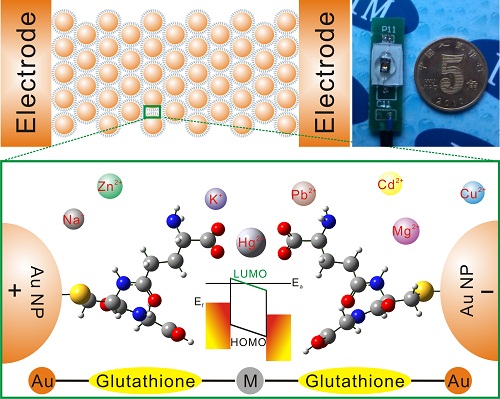
Schematic, physical and mechanism diagrams of molecular gap nanodevices with specific and sensitive responses to Pb2 +
Paper Wipe, Airlaid Paper,Hand Wipes,Kitchen Wipes
BODA ENTERPRISE LIMITED , https://www.bodapaper.com