Ink Technology Progress (I)
0 Foreword
Due to recent environmental protection legislation, the control of organic volatiles (VOC) emissions will be an important factor in the development of technology, and encourage more work on UV-curable inks and water-based inks.
More than 30 years ago, due to environmental issues, the development of these products was promoted, and research in this area has started since the 1970s. Ink must meet the need to increase production efficiency, and printing speed is generally faster and faster in all major printing processes.
Another factor that contributes to the maximum efficiency of the press is the materials and energy used.
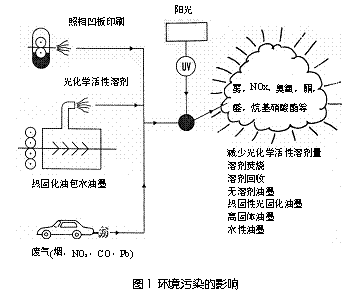
In the field of sheetfed offset lithography, accelerated drying technology has been used since the 1980s. Research on the so-called capillary absorption phase of the ink drying process on coated papers has prompted researchers to perform simple absorption tests to compare different solvents and vegetable oils, including oil chemistry as a substitute for conventional high-boiling petroleum distillation solvents. Derivative characteristics.
1 Factors Affecting Technological Development
Some of the events that took place in the 1970s that have had a major impact on the progress of ink technology are:
(1) Formulate Los Angeles 66 regulations and the resulting environmental pressure on the US ink industry. Afterwards, the study of UV-curing inks, heat-curing "solventless" inks and water-based inks was started (Figure 1).
(2) The British enacted the Working Environment Health and Safety Decree in 1974: Appeals for the use of water-based inks and coatings, which can reduce the risk of fire and improve safety, thus making the printing work environment cleaner and helping to reduce the external environment Pollution (but there were no special legislative restrictions on VOCs at the time).
(3) The raw materials of the ink industry, such as organic pigments, resins, solvents and auxiliary chemicals, are increasingly dependent on petrochemical resources. The oil crisis in the Middle East caused a shortage of raw materials and increased prices, which also prompted the use of water-based inks and coatings in areas where organic solvents were originally used for gravure printing and offset printing.
(4) The excess of organic solvents during the recession and the urgency of developing water-based alternatives disappeared.
2 UV Curing Inks and Their Applications
By the 1980s, the United States’ interest in research had slightly declined, but it had slightly increased in the UK. It was mainly applied to the narrow-stencil printing of typographic labels, paper and board, metal flat-panels and some plastic and polyethylene coatings. Plates are sheet-fed for lithographic printing and can be extended to the screen printing process so that more types of substrates and non-planar substrates can be printed and become another use for UV inks.
(2) The advantages of using UV inks in lithographic printing include: fast curing, which can be used for instant and offset printing processes; no need for powder spraying; no solvent release; no “oxidation volatility†that can result from ink types based on drying oils. And printing stability (do not dry in the machine).
(3) Compared with traditional offset printing inks, UV inks are relatively expensive, which limits the further application of UV ink technology. It has been expected that the price difference will disappear as the market for UV ink applications increases, but it has not yet been achieved.
(4) Early problems exist such as skin irritation and activation of some active acrylic monomers for UV inks. To this end, the British Printing Ink Manufacturers Association (SBPIM, now a member of the British Coatings Federation (BCF)), lists a range of monomers that are not recommended for all UV inks and coatings.

(5) Materials chemistry and technology for UV inks have continued to evolve. Developments have been made on active monomers, oligomers and prepolymers (such as epoxy, polyurethane, and polyester oligomers) and photoinitiators. Better understanding of the pigment/base material relationship, UV lamp development, and equipment.
(6) The UV over spray varnish reusability in online applications is higher than the traditional lithographic ink process (wet touch wet) and post print (wet touch dry) varnish including roller coating and screen printing process (as shown in Figure 2) Show).
(7) The use of UV inks in the label printing process of narrow screen letterpress printing presses is increasing, while the increase in the printing process of the offset printing presses is more pronounced.
(8) Another recent potential application of potential growth: UV offset printing inks are used for comic printing.
(9) UV-cured offset printing inks for printing wide-width flexible packaging materials are under development. First of all, the outstanding characteristics of the UV offset printing process are good quality and strong three-dimensionality, which can improve the design quality.
(10) With respect to free-radical UV curable inks, the development of reactive diluents is of interest, with a focus on reducing the skin irritation of these products.
(11) Research on photoinitiators to overcome potential migration issues (such as printing the outer surface of food packaging) is also underway.
Taihe Fangyuan Muye Co.,Ltd , https://www.fyofficefurniture.com